一、个人信息
| 条目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 学号 | xxxxxx |
| 姓名 | Thyrsael |
| 学院 | 计算机学院 |
| JobID | 7991086 |
二、实验过程
对于模式串的生成,调用 gen_ped 程序,生成长度为 3,周期长度为 2,随机种子为 1。调用命令如下
./gen_ped 3 2 1 pattern.dat生成字符串:
nwn然后运行主程序,采用 4 个 node 运行最终输出如下
The Text on node 0 is nwnw .
The Text on node 1 is nwnw .
The Text on node 2 is ebeb .
The Text on node 3 is gvgv .
This is the match result on node 0
(0) +
(1) -
This is the match result on node 1
(2) +
(3) -
(4) +
(5) -
This is the match result on node 2
(6) -
(7) -
(8) -
(9) -
This is the match result on node 3
(10) -
(11) -
(12) -
(13) -
三、算法流程
3.1 泳道图
该泳道图过长,如果在 PDF 中不方便查看,还可以看文件中附带的图片
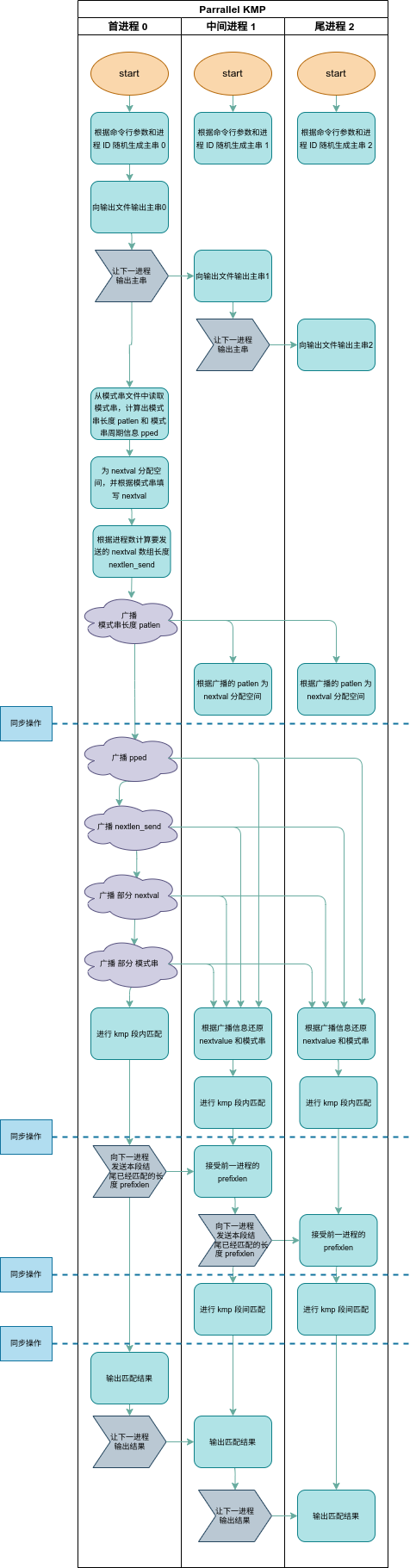
在绘制泳道图的时候,需要注意 MPI_Send, MPI_Recv, MPI_Bcast 都是阻塞通信。
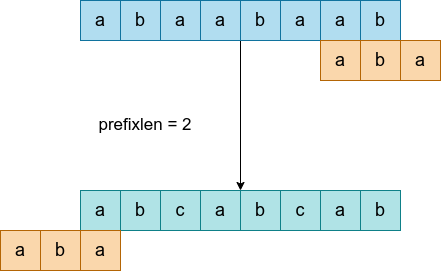
3.2 段内匹配和段间匹配
段间比配指的是,可能存在主串中的模式串横跨两个进程的段的情况,所以需要每个进程都需要向后一进程传递 prefixlen 信息,并利用前一进程传递的 prefixlen 信息进行段间匹配。也就是这样的图
3.3 还原 nextvalue
为了节省开支,我们在首进程中计算出的 nextval 和读取的 pattern 并不会完全广播,而是只广播一部分,然后利用周期信息完成还原,这就要求周期信息可以作用于还原,我们看到,主进程一般发送 pped.pedlen * 2 模式串周期长度的两倍,这是因为对于周期循环而言,两个周期就可以概括 nextval 信息。
if (numprocs > 1)
{
// 重复了不到两个周期
if (pped.pednum == 1)
{
// nextlen_send 是要发送的 next 的长度
nextlen_send = patlen;
}
else
{
nextlen_send = pped.pedlen * 2;
}
}如 abaabaabaaba 这个串,其 nextval 为
| a | b | a | a | b | a | a | b | a | a | b | a | a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 1 |
经过多次实验,确实有这个规律:其周期重复第二个周期的 nextval 值,实验代码片段如下:
#define VARNAME(var) (#var)
#define MAX_LEN 500
int next[MAX_LEN];
int nextval[MAX_LEN];
void print_array(char *array_name, int *array, int len)
{
printf("%s:\n", array_name);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%4d", array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void gen_nextval(char *pattern)
{
// 模式串长度
int pattern_len = strlen(pattern);
// nextval 填写指针,逐个递增,我们会逐个填写 nextval[nextval_cur]
int nextval_cur = 1;
// nextval[0] = -1,因为在 pattern[0] 前没有字符串
nextval[0] = -1;
// 求解 nextval
while (nextval_cur < pattern_len)
{
// 这里的迭代都是与 next 相同的
// 完全一样的意思是必须采用 next 数组迭代
int same_len = next[nextval_cur - 1];
while (!(same_len == -1 || pattern[nextval_cur - 1] == pattern[same_len]))
{
same_len = next[same_len];
}
// 只有这里发生了变化
if (pattern[nextval_cur] == pattern[same_len + 1])
{
nextval[nextval_cur] = nextval[same_len + 1];
}
else
{
nextval[nextval_cur] = same_len + 1;
}
nextval_cur++;
}
print_array(VARNAME(nextval), nextval, pattern_len + 1);
}3.4 并行计算比
3.4.1 实验记录
对于 gen_pat 采用参数 32 4 1 。
第一次实验
对于主串,采用的是 256 长度,8 周期长度的主串。
对于并行程序,采用 4 node,16 core 的配置,结果如下
The programmed has run 1.317340s对于串行程序,结果如下
The programmed has run 0.003251s可以看到串行程序的运行速度更快。
第二次实验
对于主串,采用的是 65536 长度,8 周期。
并行为 4 node,16 core
processor num = 16
textlen = 65536
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 1.168861s串行为
processor num = 1
textlen = 65536
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 0.020678s依然是串行更优。
第三次实验
对于主串,采用 16777200 长度,8 周期。
并行1:4 node, 16 core
processor num = 16
textlen = 16777200
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 3.852234s串行:
processor num = 1
textlen = 16777215
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 1.999268s并行2:1 node, 8 core
processor num = 8
textlen = 16777208
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 0.451285s并行3:4 node, 32 core
processor num = 32
textlen = 16777184
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 6.018055s并行4:4 node, 8 core
processor num = 8
textlen = 16777208
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 3.350692s并行5:1 node, 16 core
processor num = 16
textlen = 16777200
patlen= 32
The programmed has run 0.278959s3.4.2 结论
当数据规模小的时候,优化并不明显。而且不同节点的传输效率比较低,所以尽量采用一个节点。最终最大加速比为 7.167。
四、源码的修改
源码在这个位置的指针类型错误,修改即可
// error
void GetFile(char *filename, char *place, int *number)
// correct
void GetFile(char *filename, char **place, int *number)最终源码为
#include <malloc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX(m, n) (m > n? m : n)
typedef struct
{
int pedlen; // 模式串内部的周期长度
int psuffixlen; // 模式串后缀长度
int pednum; // 模式串重复周期个数
} pntype; // ped 应该是 period 周期之意 pntype 应该是 pattern type 的意思
/**
* @brief 对模式串进行周期分析,并计算相应的 new 和 newval 值
*
* @param W 模式串
* @param patlen 模式串的长度
* @param nextval nextval 数组
* @param pped 返回值
*/
void Next(char *W, int patlen, int *nextval, pntype *pped)
{
int i, j, plen;
int *next;
if ((next = (int *) malloc((patlen + 1) * sizeof(int))) == NULL)
{
printf("no enough memory\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 计算 next 和 nextval */
next[0] = nextval[0] = -1;
j = 1;
while (j <= patlen)
{
i = next[j - 1];
// 没有找到,不断递进的过程
while (i != (-1) && W[i] != W[j - 1])
{
i = next[i];
}
// 从循环中出来,意味着找到了
next[j] = i + 1;
// 利用 next 数组生成 nextVal 数组
if (j != patlen)
{
if (W[j] != W[i + 1])
{
nextval[j] = i + 1;
}
else
{
nextval[j] = nextval[i + 1];
}
}
// 递进游标
j++;
}
// 更新 pped 结构体
pped->pedlen = patlen - next[patlen];
pped->pednum = (int) (patlen / pped->pedlen);
pped->psuffixlen = patlen % pped->pedlen;
// 释放 next 空间
free(next);
}
/**
* @brief kmp 算法
*
* @param T 主串
* @param W 模式串
* @param textlen 主串长度
* @param patlen 模式串长度
* @param nextval nextval 数组
* @param pped 模式串的周期信息
* @param prefix_flag 当 prefix_flag 被置 1 的时候,只要模式串剩余的部分比主串剩余的部分多了,那么就结束算法
* @param matched_num 从哪里开始匹配的意思
* @param match 一个数组,当 match[index] == 1 时,表示主串的 index 位是符合匹配的开始
* @param prefixlen 前缀的长度
*/
void kmp(char *T, char *W, int textlen, int patlen, int *nextval, pntype *pped,
int prefix_flag, int matched_num, int *match,int *prefixlen)
{
int i, j;
// 主串游标
i = matched_num;
// 模式串游标
j = matched_num;
while (i < textlen)
{
// 当 prefix_flag 被置 1 的时候,只要模式串剩余的部分比主串剩余的部分多了,那么就结束算法
if ((prefix_flag == 1) && ((patlen - j) > (textlen - i)))
{
break;
}
// 没有匹配上的情况
while (j != (-1) && W[j] != T[i])
{
j = nextval[j];
}
// 匹配完成了
if (j == (patlen - 1))
{
// 这里应该是在主串中匹配好的模式串的首字符处置 1
match[i - (patlen - 1)] = 1;
// 应该说的是 pednum == 1 && psuffixlen == 0 的情况
if (pped->pednum + pped->psuffixlen == 1)
{
// 复位到最开始
j = -1;
}
else
{
// 这里是将 j 复位到了最后一个一个模式串周期的开始处
j = patlen - 1 - pped->pedlen;
}
}
// 移动游标
j++;
i++;
}
// prefixlen 会记录下在 kmp 函数结束的时候,模式串游标的位置
(*prefixlen) = j;
}
/**
* @brief 重构模式串以及 nextval 函数
*
* @param patlen 模式串长度
* @param pped 模式串周期信息
* @param nextval nextval 数组
* @param W 模式串
*/
void Rebuild_info(int patlen, pntype *pped, int *nextval, char *W)
{
int i;
// 如果模式串周期是 1
if (pped->pednum == 1)
{
// 从 W 的起始位置向 W[pedlen] 拷贝 suffixlen 个字符
memcpy(W + pped->pedlen, W, pped->psuffixlen);
}
else
{
// 第二个周期只需要拷贝模式串,不需要拷贝 nextValue
memcpy(W + pped->pedlen, W, pped->pedlen);
// 这里其实改成 i = 2 更好理解
for (i = 2; i < pped->pednum; i++)
{
memcpy(W + i * pped->pedlen, W, pped->pedlen);
memcpy(nextval + i * pped->pedlen, nextval + pped->pedlen, pped->pedlen * sizeof(int));
}
// 拷贝后缀
if (pped->psuffixlen != 0)
{
memcpy(W + i * pped->pedlen, W, pped->psuffixlen);
memcpy(nextval + i * pped->pedlen, nextval + pped->pedlen, pped->psuffixlen * sizeof(int));
}
}
}
/**
* @brief 生成文本串
* seed 是每个进程的 ID,所以每个进程的生成的字符串是不一样的
*/
void gen_string(int strlen, int pedlen, char *string, int seed)
{
int suffixlen, num, i, j;
srand(seed);
// 按照 pedlen 随机生成一个串
for (i = 0; i < pedlen; i++)
{
num = rand() % 26;
string[i] = 'a' + num;
}
// 将 ped 复制多次
for (j = 1; j < strlen / pedlen; j++)
{
strncpy(string + j * pedlen, string, pedlen);
}
// 如果没有复制完,那么就在后缀补充一部分
if ((suffixlen = strlen % pedlen) != 0)
{
strncpy(string + j * pedlen, string, suffixlen);
}
}
/**
* @brief Get the File object 从文件读入模式串信息
*
* @param filename 文件名
* @param place 文件的信息存储于其指向的内存
* @param number 文件的大小
*/
void GetFile(char *filename, char **place, int *number)
{
FILE *fp;
struct stat statbuf;
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "rb")) == NULL)
{
printf("Error open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
// fileno 可以获得文件描述符,就是 stdin = 0, stdout = 1 的那个 int 值
// 获得文件的状态
fstat(fileno(fp), &statbuf);
// st_size 是文件的大小,这里按照文件的大小给 place 分配空间
if (((*place) = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * statbuf.st_size)) == NULL)
{
printf("Error alloc memory\n");
exit(1);
}
// 1 个字节 1 个字节读入,读入 st_size 次
if (fread((*place), 1, statbuf.st_size, fp) != statbuf.st_size)
{
printf("Error in reading num\n");
exit(0);
}
fclose(fp);
(*number) = statbuf.st_size;
}
/**
* @brief 清空文件(因为其他写文件操作都是 a 追加,所以会导致重复运行的时候多次结果重复)
*
* @param filename 文件名
*/
void ClearFile_info(char *filename)
{
FILE *fp;
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "w")) == NULL)
{
printf("Error open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
fclose(fp);
}
/**
* @brief 打印运行参数信息
* T 是要打印的信息
* id 是进程编号
*/
void PrintFile_info(char *filename, char *T, int id)
{
FILE *fp;
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "a")) == NULL)
{
printf("Error open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
fprintf(fp, "The Text on node %d is %s .\n", id, T);
fclose(fp);
}
/**
* @brief 打印匹配结果
*
* @param filename 文件名
* @param t match 数组,置 1 说明匹配成功
* @param len match 长度
* @param init 起始位置,因为需要一个统一的标号
* @param id 进程 id
*/
void PrintFile_res(char *filename, int *t, int len, int init, int id)
{
FILE *fp;
int i;
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "a")) == NULL)
{
printf("Error open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
fprintf(fp, "This is the match result on node %d \n", id);
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (t[i] == 1)
{
fprintf(fp, "(%d) +\n", i + init);
}
else
{
fprintf(fp, "(%d) -\n", i + init);
}
}
fclose(fp);
}
void main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// T 是主串的一部分,W 是模式串全部
char *T, *W;
// nextval 是 kmp 的关键,match 记录着匹配好的首下标
int *nextval, *match;
// textlen 是部分主串的长度,patlen 是模式串长度,pedlen 是模式串重复周期长度,nextlen_send 是广播的 nextvalue 的长度
int textlen, patlen, pedlen, nextlen_send;
// 记录着模式串的周期信息
pntype pped;
// prefixlen 是已经完成匹配的长度
int i, myid, numprocs, prefixlen, ready;
// 记录时间
double start_time, end_time;
MPI_Status status;
// 初始化进程间通信
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &numprocs);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);
if (myid == 0)
{
start_time = MPI_Wtime();
}
nextlen_send = 0;
ready = 1;
// 读取命令行参数,计算文本的长度
textlen = atoi(argv[1]);
textlen = textlen / numprocs;
pedlen = atoi(argv[2]);
// 分配空间
if ((T = (char *) malloc(textlen * sizeof(char))) == NULL)
{
printf("no enough memory\n");
exit(1);
}
// 生成字符串, T 中存着生成的字符串,这个字符串应该是主串
// 因为 seed 是 myid,所以每个进程生成的主串是不同的
gen_string(textlen, pedlen, T, myid);
// 依次打印每个进程生成的主串
if (myid == 0)
{
ClearFile_info("match_result");
PrintFile_info("match_result", T, myid);
// 如果进程大于 1,那么就发送信息
if (numprocs > 1)
{
MPI_Send(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, 1, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
}
else
{
// 接受来自上一个进程的 ready 信息,然后发送给下一个进程
MPI_Recv(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, myid - 1, myid - 1, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
PrintFile_info("match_result", T, myid);
// 只要不是最后一个进程,都发送信息
if (myid != numprocs - 1)
{
MPI_Send(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, myid + 1, myid, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
}
printf("\n");
// 每个主串的匹配信息被记录于此
if ((match = (int *) malloc(textlen * sizeof(int))) == NULL)
{
printf("no enough memory\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 处理器 0 读入模式串,并记录运行参数 */
if (myid == 0)
{
printf("processor num = %d \n", numprocs);
// 从这里可以看出,本质上的主串是每个进程生成主串后拼接在一起的
printf("textlen = %d\n", textlen * numprocs);
// 从 pattern.dat 中读取信息,字符串存储在 W 中
GetFile("pattern.dat", &W, &patlen);
printf("patlen= %d\n", patlen);
if ((nextval = (int *) malloc(patlen * sizeof(int))) == NULL)
{
printf("no enough memory\n");
exit(1);
}
/* 对模式串进行分析,对应于算法 14.6步骤(1)*/
Next(W, patlen, nextval, &pped);
if (numprocs > 1)
{
// 重复了不到两个周期
if (pped.pednum == 1)
{
// nextlen_send 是要发送的 next 的长度
nextlen_send = patlen;
}
else
{
nextlen_send = pped.pedlen * 2;
}
}
}
/*向各个处理器播送模式串的信息,对应于算法 14.6步骤(2)*/
if (numprocs > 1)
{
// 主进程广播出去了模式串长度
// Bcast 是阻塞的
MPI_Bcast(&patlen, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 对于从进程
if (myid != 0)
{
// 按照广播得到的模式串长度 patlen 给 nextVal 和 W 模式串分配空间
if (((nextval = (int *) malloc(patlen * sizeof(int))) == NULL)
|| ((W = (char *) malloc(patlen * sizeof(char))) == NULL))
{
printf("no enough memory\n");
exit(1);
}
}
// 同步
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 主进程向从进程广播各种信息
// 3 是因为 pntype 的大小就是 3 个 int
MPI_Bcast(&pped, 3, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Bcast(&nextlen_send, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// nextVal 串一般只发送了两个周期
MPI_Bcast(nextval, nextlen_send, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 模式串只发送了一个周期的长度
MPI_Bcast(W, pped.pedlen, MPI_CHAR, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
/*调用修改过的 KMP 算法进行局部串匹配,对应于算法14.6步骤(3)*/
if (numprocs == 1)
{
kmp(T, W, textlen, patlen, nextval, &pped, 1, 0, match + patlen - 1, &prefixlen);
}
else
{
// 对于从进程,还原模式串和 nextval 数组
if (myid != 0)
{
/*各个处理器分别根据部分串数据以及周期信息重构模式串*/
Rebuild_info(patlen, &pped, nextval, W);
}
// 进行段内匹配
if (myid != numprocs - 1)
{
kmp(T, W, textlen, patlen, nextval, &pped, 0, 0, match + patlen - 1, &prefixlen);
}
else
{
// 只有尾进程的 prefix_flag 为 1,表示只有最后一个进程不需要保留 prefixlen 信息
kmp(T, W, textlen, patlen, nextval, &pped, 1, 0, match + patlen - 1, &prefixlen);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 开始进行段间匹配
// 除了最后一个进程,都需要向后发送处理信息,这里发送的是 prefixlen
if (myid < numprocs - 1)
{
MPI_Send(&prefixlen, 1, MPI_INT, myid + 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
// 除了第一个进程,都需要向前接受处理信息
if (myid > 0)
{
MPI_Recv(&prefixlen, 1, MPI_INT, myid - 1, 99, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// 除了第一个进程,都需要进行段间匹配
if ((myid > 0) && (prefixlen != 0))
{
kmp(T - prefixlen, W, prefixlen + patlen - 1, patlen, nextval, &pped, 1, prefixlen,
match + patlen - 1 - prefixlen, &prefixlen);
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
// 输出匹配结果
if (myid == 0)
{
PrintFile_res("match_result", match + patlen - 1, textlen - patlen + 1, 0, myid);
if (numprocs > 1)
{
MPI_Send(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, 1, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
}
else
{
MPI_Recv(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, myid - 1, myid - 1, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
PrintFile_res("match_result", match, textlen, myid * textlen - patlen + 1, myid);
if (myid != numprocs - 1)
{
MPI_Send(&ready, 1, MPI_INT, myid + 1, myid, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
}
free(T);
free(W);
free(nextval);
if (myid == 0)
{
end_time = MPI_Wtime();
printf("The programmed has run %lfs\n", end_time - start_time);
}
MPI_Finalize();
}